Get To Know About Boils And Be Free From It Today
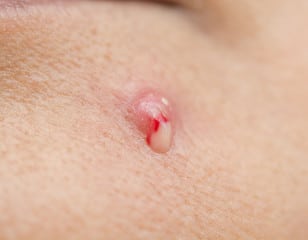
What Is a Boil?

A boil is a skin infection that starts in a hair follicle or oil gland. Also referred to as a skin abscess, it is a localized infection deep in the skin. Boils can be as small as a pea or as large as a golf ball and can develop on any part of the body. A boil generally starts as a reddened, tender area. Over time, the area becomes firm and hard. Eventually, the center of the abscess softens and becomes filled with infection-fighting white blood cells that the body sends via the bloodstream to eradicate the infection. This collection of white blood cells, bacteria, and proteins is known as pus. Finally, the pus “forms a head,” which can be surgically opened or spontaneously drain out through the surface of the skin.
Boil Symptoms
A boil starts as a hard, red, painful lump usually less than an inch in size. Over the next few days, the lump becomes softer, larger, and more painful. Soon a pocket of pus forms on the top of the boil.
Signs of a severe infection are ;
- The skin around the boil becomes red, painful, and swollen;
- More boils may appear around the original one;
- A fever develops
- The lymph nodes in the area become swollen.
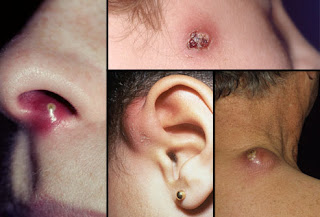
Where Do Boils Form?
The most common places for boils to appear are on the
- neck,
- armpits,
- shoulders,
- buttocks,
- eyelid (when one forms on the eyelid, it is called a sty.)
What Causes Boils?
There are many causes of boils. Boils are usually caused by a type of bacteria called Staphylococcus (staph). This germ can be present on normal skin and enters the body through tiny breaks in the skin or by traveling down a hair to the follicle. Some boils can be caused by an ingrown hair.
Others can form as the result of a splinter or other foreign material that has become lodged in the skin that causes the infection to develop. Others boils, such as those of acne, are caused by plugged sweat glands that become infected.
The skin is an essential part of our immune defense against materials and microbes that are foreign to our body. Any break in the skin, such as a cut or scrape, can develop into an abscess (boil) should it then become infected with bacteria.
What Is the Treatment for a Boil?
The primary treatment for most boils is heat application, usually with hot soaks or hot packs. Heat application increases the circulation to the area and allows the body to better fight off the infection by bringing antibodies and white blood cells to the site of infection.
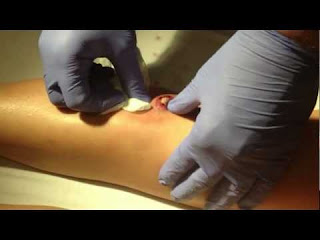
Another method of treating boil is to wash the drained boil with antibacterial soap. Once the boil starts draining, it is very important that you keep the area clean. Wash the boil thoroughly with an antibacterial soap and warm water, until all of the pus has drained. Once clean, dry the boil with a clean towel or some paper towel, which should be washed or thrown away immediately after use, to avoid spreading the infection.
As the surface of the boil softens and fills with pus, it may be tempting to burst the skin with a needle and drain the contents yourself. However, this is not recommended as it can cause the boil to become infected or the bacteria within the boil to spread, causing multiple boils.
What Can Be Done to Prevent Boils ?
Practice good hygiene.
Good hygiene is probably the most important thing you can do to prevent boils As boils are usually caused by bacteria infecting the hair follicles, you should prevent the build up of bacteria on the surface of the skin by washing daily. Normal soap is fine, but if you are prone to developing boils, an antibacterial wash may be better.
Frequent Questions People Asked About Me Boil
1. Are Boils Contagious?
Boils themselves are not contagious, but the bacteria that cause boils are. Until it drains and heals, an active skin boil is contagious. The infection can spread to other parts of the person’s body or to other people through skin-to-skin contact or the sharing of personal items.
As long as the boil is small and firm, opening the area and draining the boil is not helpful, even if the area is painful. However, once the boil becomes soft or “forms a head” (that is, a small pustule is noted in the boil), it can be ready to drain. Once drained, pain relief can be dramatic. Most small boils, such as those that form around hairs, drain on their own with soaking and/or heat application. On occasion, and especially with larger boils, the larger boil will need to be drained or “lanced” by a health-care practitioner. Frequently, these larger boils contain several pockets of pus that must be opened and drained.
3. When Should I Seek Medical Attention?
You should call your doctor and seek medical attention if:
- the boil is located on your face, near your spine, or near your anus;
- a boil is getting larger;
- the pain is severe;
- you have a fever;
- the skin around the boil turns red or red streaks appear;
- you have a heart murmur, diabetes, any problem with your immune system, or use immune-suppressing drugs (for example, corticosteroids or chemotherapy) and you develop a boil;
- the boil has not improved after five to seven days of home treatment;
- you get many boils over several months.
Don’t forget to take good care of your body. Stay healthy always.


Wow great article and I will share this with my friends and family members thanks
Thanks Mathias, for visiting Sound Health Doctor. It's a pleasure having you around.
Don't forget to share to your people, you could save a life through this.
Great article on health care, it's often said that a healthy live is worth than anything else. Thank for sharing
Thanks to God. I dont have something like this in my family and will be always careful not to have such. Weldone healthdoctor
Its good you don't have something like that in your family and I pray you will never have.
You could share with your friends, you don't know who might be experiencing it, you might save a life by sharing.
Thanks for Visiting Sound Health Doctor. It's a pleasure. We hope you visit more often so as to get tips to make you live a healthier life.
True fact you said, AbdulMalik. A healthy life is worth more than anything.
Thanks for visiting Sound Health Doctor. We hope to see more of your comments on our other posts.
Things we do not know tends to really affect us. I can gladly say i learnt alot from this piece of article.
Eames, you made a nice point there and I'm glad to hear that you learnt from this article.
Thanks for visiting Sound Health Doctor.
The article has actually peaks my interest. I’m going to bookmark your site and keep checking for new info.